Software rasterization: a fast and accurate algorithm for rasterizing triangles in C
Перевод этой статьи на русском
The basis of three-dimensional graphics is triangle rasterization algorithm. In this article, I explain how a software triangle rasterization works in my own game engine.
First, I will present the full algorithm, and then we’ll break it down in detail:
static void SwapFloat(float* a, float* b) { float c = *a; *a = *b; *b = c; }
void DrawTriangle(
float ax, float ay, float az, float au, float av,
float bx, float by, float bz, float bu, float bv,
float cx, float cy, float cz, float cu, float cv
) {
// For every vertex:
// x, y - screen coordinates
// z - depth
// u, v - texture coordinates
// Sort vertices by y-coordinate ascending (y1 <= y2 <= y3)
if (ay > by) {
// swap(a, b)
SwapFloat(&ax, &bx);
SwapFloat(&ay, &by);
SwapFloat(&az, &bz);
SwapFloat(&au, &bu);
SwapFloat(&av, &bv);
}
if (ay > cy) {
// swap(a, c)
SwapFloat(&ax, &cx);
SwapFloat(&ay, &cy);
SwapFloat(&az, &cz);
SwapFloat(&au, &cu);
SwapFloat(&av, &cv);
}
if (by > cy) {
// swap(b, c)
SwapFloat(&bx, &cx);
SwapFloat(&by, &cy);
SwapFloat(&bz, &cz);
SwapFloat(&bu, &cu);
SwapFloat(&bv, &cv);
}
// Round y-coordinates and clamp to screen bounds
int y_min = max( (int)ceilf(ay - 0.5f), 0);
int y_mid = min(max((int)ceilf(by - 0.5f), 0), screen_height);
int y_max = min( (int)ceilf(cy - 0.5f), screen_height);
// Prepare values for perspective-correct interpolation
az = 1.0f / az;
bz = 1.0f / bz;
cz = 1.0f / cz;
au *= az;
av *= az;
bu *= bz;
bv *= bz;
cu *= cz;
cv *= cz;
// Rasterize triangle scanlines
for (int y = y_min; y < y_max; y++) {
float pixel_center = (float)y + 0.5f;
float lt, lx, lz, lu, lv; // left edge
float rt, rx, rz, ru, rv; // right edge
// Calculate left edge
lt = (pixel_center - ay) / (cy - ay);
lx = ax + (cx - ax) * lt;
lz = az + (cz - az) * lt;
lu = au + (cu - au) * lt;
lv = av + (cv - av) * lt;
// Determine if we are in the first or the second half of the triangle
if (y < y_mid) {
// Calculate right edge (first half)
rt = (pixel_center - ay) / (by - ay);
rx = ax + (bx - ax) * rt;
rz = az + (bz - az) * rt;
ru = au + (bu - au) * rt;
rv = av + (bv - av) * rt;
} else {
// Calculate right edge (second half)
rt = (pixel_center - by) / (cy - by);
rx = bx + (cx - bx) * rt;
rz = bz + (cz - bz) * rt;
ru = bu + (cu - bu) * rt;
rv = bv + (cv - bv) * rt;
}
// Ensure "l" is always to the left of "r"
if (lx > rx) {
// swap(l, r)
SwapFloat(&lx, &rx);
SwapFloat(&lz, &rz);
SwapFloat(&lu, &ru);
SwapFloat(&lv, &rv);
}
// Round x-coordinates and clamp to screen bounds
int ilx = (int) ceilf(lx - 0.5f); // top-left rule: ceil to include left edge
int irx = (int)floorf(rx - 0.5f); // top-left rule: floor to exclude right edge
int x_min = max(ilx, 0);
int x_max = min(irx + 1, screen_width);
// Loop over the horizontal range of the current scanline
for (int x = x_min; x < x_max; x++) {
int i = (y * screen_width) + x;
float t = (float)(x - ilx) / (rx - lx); // x interpolation factor (0.0 - 1.0)
float z = lz + (rz - lz) * t;
if (z > screen_depth[i]) {
float u = (lu + (ru - lu) * t) / z;
float v = (lv + (rv - lv) * t) / z;
screen_color[i] = SampleTextureColor(texture, u, v);
screen_depth[i] = z;
}
}
}
}
Algorithm Breakdown
We fill perform scanline rasterization - drawing pixels row by row to ensure linear memory access for cache efficiency.
1. Sort vertices by y-coordinate
if (ay > by) { SwapPoint(&a, &b); }
if (ay > cy) { SwapPoint(&a, &c); }
if (by > cy) { SwapPoint(&b, &c); }
Let's start by sorting the vertices by y-coordinate. So we have this order: a - min, b - middle, c - max. This splits the triangle into upper and lower parts, simplifying edge calculation.
2. Top-left filling convention
To avoid gaps between adjacent triangles, use consistent rounding: round y - 0.5 up for y, round left x using ceil up and right x using floor down. This matches Vulkan and DirectX conventions:
// ...
// Before y loop:
int y_min = (int)ceilf(ay - 0.5f);
int y_mid = (int)ceilf(by - 0.5f);
int y_max = (int)ceilf(cy - 0.5f);
// ...
// Before x loop:
int x_min = (int) ceilf(lx - 0.5f); // top-left rule: ceil to include left edge
int x_max = (int)floorf(rx - 0.5f); // top-left rule: floor to exclude right edge
3. Perspective‑correct interpolation
az = 1.0f / az;
bz = 1.0f / bz;
cz = 1.0f / cz;
au *= az;
av *= az;
bu *= bz;
bv *= bz;
cu *= cz;
cv *= cz;
We invert z (1/z) and multiply texture coords (u, v) by 1/z before interpolation. Without this step, textures appear distorted (as in PS1 graphics).
4. Y-loop
for (int y = y_min; y < y_max; y++) {
...
}
For each scanline, compute segment start (lx) and end (rx) x-coordinates.
Left edge is always from A → C (min to max):
lt = (pixel_center - ay) / (cy - ay);
lx = ax + (cx - ax) * lt;
lz = az + (cz - az) * lt;
Right edge from either A → B (upper part) or B → C (lower part) based on the current y:
if (y < y_mid) {
rt = (center_y - ay) / (by - ay);
rx = ax + (bx - ax) * rt;
rz = az + (bz - az) * rt;
// ...
} else {
rt = (center_y - by) / (cy - by);
rx = bx + (cx - bx) * rt;
rz = bz + (cz - bz) * rt;
// ...
}
5. Ensure correct edge ordering
Swap left/right if needed to maintain left <= right.
if (lx > rx) { SwapFloat(&lx, &rx); SwapFloat(&lz, &rz); }
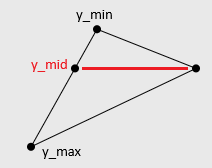
6. X-loop
For each x on the scanline, interpolate depth z, compare it to the z-buffer, and if closer, interpolate texture coords (u, v) with perspective correction and sample the texture.:
for (int x = x_min; x < x_max; x++) {
int i = (y * screen_width) + x;
float t = (float)(x - ilx) / (rx - lx); // x interpolation factor (0.0 - start, 1.0 - end)
float z = lz + (rz - lz) * t; // depth
if (z > screen_depth[i]) { // depth-test
screen_color[i] = 0xFFFFFF;
screen_depth[i] = z;
}
}
7. Vertex attribute extensibility
The algorithm can handle additional per-vertex attributes (e.g. lighting factor l, extra UVs for multitexturing or lightmaps). Just treat them like z or uv.
8. Optimizations
Я намеренно упростил код, представленный в начале статьи, чтобы улучшить его читабельность в угоду производительности. Если вы дочитали до этого момента и вас интересует дальнейшая оптимизация, то ниже вы найдете финальную версию алгоритма для реального рендерера:
static void DrawTriangle_Span(
const Texture *texture,
int y,
float lx, float lz, float la, float lb, float lc,
float rx, float rz, float ra, float rb, float rc
) {
// Ensure "l" is always to the left of "r"
if (lx > rx) {
SwapFloat(&lx, &rx);
SwapFloat(&lz, &rz);
SwapFloat(&la, &ra);
SwapFloat(&lb, &rb);
SwapFloat(&lc, &rc);
}
// Precalculate spans
float span_x = rx - lx;
if (span_x <= 0.0f) {
return; // skip if no pixels to draw
}
float span_z = rz - lz;
float span_a = ra - la;
float span_b = rb - lb;
float span_c = rc - lc;
// Round and x-coordinates to screen bounds
int ilx = (int) ceilf(lx - 0.5f); // top-left rule: ceil to include left edge
int irx = (int)floorf(rx - 0.5f); // top-left rule: floor to exclude right edge
int nlx = max(ilx, 0);
int nrx = min(irx + 1, screen_width);
// Get scanline pointers
int i = (screen_width * y) + nlx;
WORD *color_ptr = &screen_color[i];
float *depth_ptr = &screen_depth[i];
// Loop over the horizontal range of the current scanline
for (int x = nlx; x < nrx; x++) {
// Interpolate z
float t = (float)(x - ilx) / span_x;
float z = lz + span_z * t;
// Depth test
if (z > *depth_ptr) {
// Perspective-correct interpolation
float u = (la + span_a * t) / z;
float v = (lb + span_b * t) / z;
float l = (lc + span_c * t) / z;
// Sample texture color
WORD color = SampleTexture(texture, u, v);
// Transparency-bit test
if (color & COLOR16_MASK_A) {
// Apply lighting
color = Color_ApplyLighting(color, l);
*color_ptr = color;
*depth_ptr = z;
}
}
// Step scanline pointers
color_ptr++;
depth_ptr++;
}
}
void DrawTriangle(
const Texture *texture,
float x1, float y1, float z1, float a1, float b1, float c1,
float x2, float y2, float z2, float a2, float b2, float c2,
float x3, float y3, float z3, float a3, float b3, float c3
) {
// Prepare the triangle vertices for perspective-correct texture interpolation
z1 = 1.0f / z1;
z2 = 1.0f / z2;
z3 = 1.0f / z3;
a1 *= z1;
b1 *= z1;
c1 *= z1;
a2 *= z2;
b2 *= z2;
c2 *= z2;
a3 *= z3;
b3 *= z3;
c3 *= z3;
// Sort vertices by y-coordinate ascending (y1 <= y2 <= y3)
if (y1 > y2) {
SwapFloat(&x1, &x2);
SwapFloat(&y1, &y2);
SwapFloat(&z1, &z2);
SwapFloat(&a1, &a2);
SwapFloat(&b1, &b2);
SwapFloat(&c1, &c2);
}
if (y1 > y3) {
SwapFloat(&x1, &x3);
SwapFloat(&y1, &y3);
SwapFloat(&z1, &z3);
SwapFloat(&a1, &a3);
SwapFloat(&b1, &b3);
SwapFloat(&c1, &c3);
}
if (y2 > y3) {
SwapFloat(&x2, &x3);
SwapFloat(&y2, &y3);
SwapFloat(&z2, &z3);
SwapFloat(&a2, &a3);
SwapFloat(&b2, &b3);
SwapFloat(&c2, &c3);
}
// Round y-coordinates and clamp to screen bounds
int y_min = max( (int)ceilf(y1 - 0.5f), 0);
int y_mid = min(max((int)ceilf(y2 - 0.5f), 0), screen_height);
int y_max = min( (int)ceilf(y3 - 0.5f), screen_height);
// Precalculate edges
float dy13 = y3 - y1;
float dx13 = x3 - x1;
float dz13 = z3 - z1;
float da13 = a3 - a1;
float db13 = b3 - b1;
float dc13 = c3 - c1;
float dy12 = y2 - y1;
float dx12 = x2 - x1;
float dz12 = z2 - z1;
float da12 = a2 - a1;
float db12 = b2 - b1;
float dc12 = c2 - c1;
float dy23 = y3 - y2;
float dx23 = x3 - x2;
float dz23 = z3 - z2;
float da23 = a3 - a2;
float db23 = b3 - b2;
float dc23 = c3 - c2;
#pragma omp parallel
{
// Draw the top part of the triangle
#pragma omp for
for (int y = y_min; y < y_mid; y++) {
float pixel_center = (float)y + 0.5f;
float lt = (pixel_center - y1) / dy13;
float rt = (pixel_center - y1) / dy12;
DrawTriangle_Span(
texture, y,
x1 + dx13 * lt,
z1 + dz13 * lt,
a1 + da13 * lt,
b1 + db13 * lt,
c1 + dc13 * lt,
x1 + dx12 * rt,
z1 + dz12 * rt,
a1 + da12 * rt,
b1 + db12 * rt,
c1 + dc12 * rt
);
}
// Draw the bottom part of the triangle
#pragma omp for
for (int y = y_mid; y < y_max; y++) {
float pixel_center = (float)y + 0.5f;
float lt = (pixel_center - y1) / dy13;
float rt = (pixel_center - y2) / dy23;
DrawTriangle_Span(
texture, y,
x1 + dx13 * lt,
z1 + dz13 * lt,
a1 + da13 * lt,
b1 + db13 * lt,
c1 + dc13 * lt,
x2 + dx23 * rt,
z2 + dz23 * rt,
a2 + da23 * rt,
b2 + db23 * rt,
c2 + dc23 * rt
);
}
}
}
Thank you for reading! I hope you find this algorithm useful in your projects.